Donnerstag, 1. November 2018
Moringa oleifera oil: from traditional medicine to modern cosmetics
Moringa oil is our "oil of the month" for November 2018. This means, we have an attractive discount on this oil through the whole month of November.
Click here for our oil of the month in October 2018
Moringa plant: the miracle tree
There are at least 13 species of moringa and moringa oleifera is the most prominent and the most widely cultivated and reasearched species. Moringa oleifera is a fast growing tree, resistant to draught that can grow to a height of 12 meter.
Native to sub-Himalayan regions of India and Pakistan, it is now being cultivated in other tropical and subtropical parts of the world. Its existence dates back to 150 BCC.
Leaves, fruits, flowers and pods are edible and contain various concentrations of proteins, lipids, carbohydrates and fibers as well as secondary metabolites such as: flavonoids, phenolic acids, vanillin, glucosinolates, chlorogenic acid, ferulic acid, gallic acid, quercetin, kaempferol and ellagic acid. At least 19 amino acids have been identified in the plant.
Moringa tree is known as the miracle tree because of its various nutritional, medicinal and economical properties. The name "moringa" is derived from Tamil but this tree is known under different names in different parts of the world such as drumstick tree or horseradish tree.
One of its most valuable industrial properties is coagulating properties of the seeds (thanks to a cationic protein). This property is used in rural areas of Pakistan and India to coagulate suspended organic material in water and prepare water (which is extremely rare and valuable in these regions) for household and drinking applications. Because moringa seeds (or rather the protein extracted from the seeds) have a higher pH stability compared to aluminium sulfate (the most widely used coagulating agent in the modern water treatment), they are now being used in modern aquaculture waste water treatment.
Another industrial application for the seeds (which has lead to its large-scale cultivation) is bio-diesel but this is out of the scope of this blog post.
In folklore medicine flowers, leaves and roots are used for the treatment of ascites, rheumatism and venomous bites as well as for circulatory stimulation.
Modern research confirms the folklore uses and adds other properties to this magical plant:
anti-inflammatory, diuretic, antihypertensive, antioxidant, antitumor, antiarthritic, antispasmodic, antiurolithic, hepatoprotective, anaphylactic, antihyperglycemic, antifungal, radioprotective, nephroprotective and antiulcer to name a few properties.
Moringa oil
INCI: Moringa oleifera seed oil
CAS# 93165-54-9
EINECS# 296-941-1
Iodine value: 65-72
Sap. value: 192 mg KOH/gr
The oil is derived from the seeds either by pressing or solvent extraction. The yield of the solvent extraction is obviously several times higher than cold processing but we use only cold pressed oil in hair & skin care.
Moringa oil has an intensive yellow colour and a pleasant, nutty scent. It has a very pleasant skin feel.
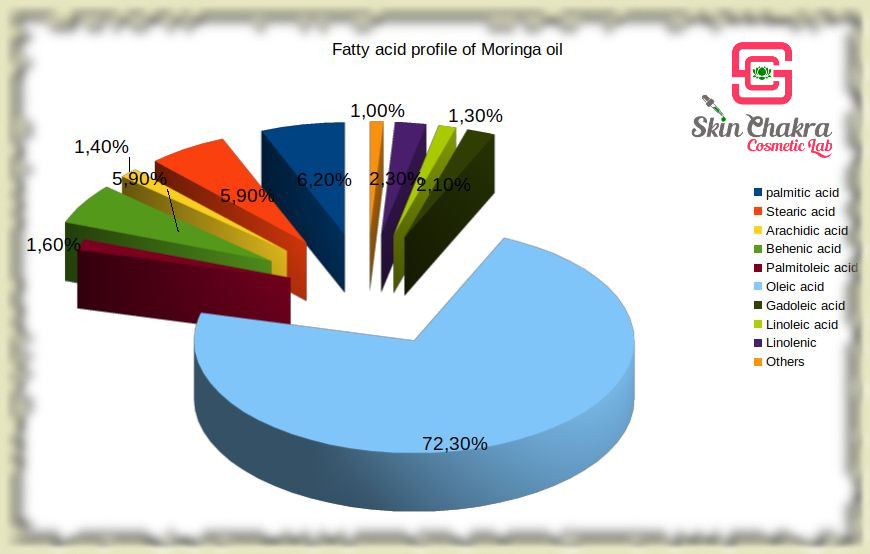
Oleic acid is the dominant fatty acid in the oil. Despite its high concentration, the oil does not feel greasy even when applied directly and pure over the skin. What makes this oil outstanding and quite different to other high oleic-acid rich plant oils is the high concentration of behenic acic (a saturated fatty acid with C22:0 structure) and palmitic acid (a saturated fatty acid with C16:0 structure). These two saturated fatty acids contribute to the covering and protecting properties of moringa oil (both hair and skin care) without any undesirable greasiness.
Moringa oil has a rather low concentration of tocopherols (Ca. 300 ppm total tocopherols with alpha and delta tocopherols being the dominant forms). Despite low tocopherol content, it has a high thermal and oxidative stability and has been used for centuries as a cooking oil in the sub-Himalayan regions (look at the low iodine value). It is even added to sunflower oil and soybean oil to improve their thermal and oxidative stability.
It has a thermal and oxidative stability comparable to castor oil yet the skin feel and the slip is much superior to castor oil. This allows the application of moringa oil in high performance hair & skin care products, specially in hot process formulations. Apart from that and because of the high thermal stability, moringa oil could be used as a carrier oil for hot extraction/maceration of plant metabolites.
| Tocopherol | mg/kg (ppm) |
| alpha-tocopherol | 125 |
| beta-tocopherol | - |
| gamma-tocopherol | 65 |
| delta-tocopheol | 105 |
Its phytosterols content is however quite remarkable with beta-sitosterole as the dominant component.
| Phytosterols | mg/kg (ppm) |
| beta-sitosterol | 480 |
| Campesterol | 160 |
| Delta-5-avenasterol | 105 |
| Stigmasterol | 180 |